Ur, Iraq
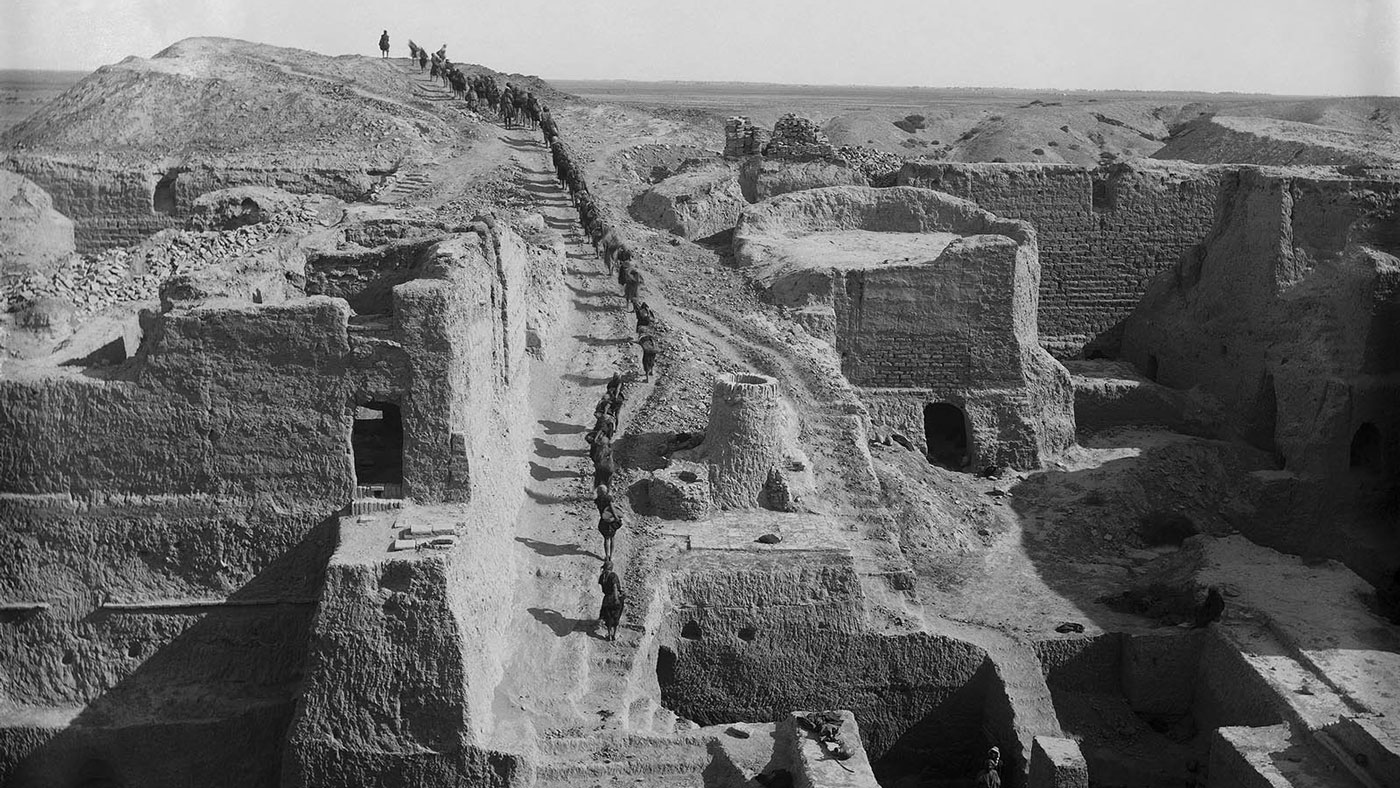

Located in southern Iraq, near the former northern limits of the Persian Gulf, Ur was one of the most famous archaeological excavations—along with Tutankhamun’s tomb in Egypt—during the early 20th century. Frequently described in the popular press, the work at Ur brought the magic of archaeology to life, particularly by tying the discoveries into familiar biblical stories. Between 1922 and 1934, the Joint Expedition of the British Museum and the Penn Museum was directed by C. Leonard Woolley and uncovered some of the most well-known and celebrated art from ancient Mesopotamia. These finds were divided between the two partner institutions (25% each) and the Baghdad Museum in Iraq (50%).
- Object[336]
- babylonian[1]
- near eastern[335]
- amulet[11]
- arrowheads[1]
- ball[1]
- balls[1]
- bead[32]
- bead spacer[1]
- beads[7]
- blade fragment[10]
- blade fragments[2]
- bone fragment[1]
- bowl[15]
- bowl sherd[1]
- celt[4]
- cylinder seal[12]
- door socket[1]
- duck weight[1]
- eye bead[1]
- figurine[1]
- fragments[1]
- game piece[7]
- grinder[8]
- hand axe[1]
- handle[1]
- implement[2]
- inlay[8]
- jar[3]
- knife handle[1]
- metal fragment[1]
- nail[1]
- object[9]
- objects[1]
- ornament[1]
- pedestal[1]
- pendant[8]
- pin fragment[1]
- pot[2]
- raw material[3]
- relief[1]
- rod[1]
- rubbing stone[1]
- sling stone[1]
- spacer[1]
- spindle whorl[1]
- stamp seal[3]
- statue fragment[1]
- stela[3]
- stone[7]
- stone fragment[7]
- string of beads[9]
- ur-namu stele[102]
- vase[1]
- vase sherd[1]
- vessel stand[1]
- weight[33]
- weights[3]
- whetstone[11]
- wreath[1]
- assyrian[1]
- early dynastic iii[8]
- early dynastic iiib[1]
- jemdet nasr[4]
- jemdet nasr period[1]
- kassite[1]
- minor dynasty[4]
- pre-flood[1]
- prehistoric[3]
- sargonic[1]
- ur i[1]
- ur iii[2]
- -3 metres below surface; pg[1]
- diqdiqqeh[1]
- found 3 1/2 to 5 1/2 m. below brick pavement dated ca. 3100 b.c. in the prehistorical settlement. between flood and royal graves. at n.w. limit of p.g.[1]
- found 5 1/2 to 6 m. below brick pavement dated ca. 3100 b.c. in the prehistorical settlement. transition from post to pre flood levels. p.g. n.w.[1]
- found 7 1/2 to 8 m. below brick pavement dated ca. 3100 b.c. in the prehistoric settlement. p.g. n.w.[2]
- house 30/e below floor level, in filling above bur-sin se annex, room 8 b.c.[1]
- jemdet nasr. disturbed grave pg 14 metres.[1]
- p.f.t. d 5 , - 590[1]
- p.f.t. d 6. - 530[1]
- pft - 900[1]
- pft, - 750 to 800[1]
- pg 1136[2]
- pg 1195[1]
- pg 1237/67[1]
- ur - pg 1163 case 34, tray 3[1]
- ampulla libra[1]
- angel[3]
- angel?[1]
- animal[1]
- arm[3]
- beard[1]
- building[1]
- bull[5]
- butcher[1]
- calf[1]
- chariot wheel[1]
- crescent[3]
- deity[2]
- demon[1]
- demon face[1]
- dog[1]
- dress[1]
- eye[1]
- field[1]
- figure[2]
- fly?[1]
- gate[1]
- gilgamesh[1]
- goat[1]
- god[3]
- goddess[2]
- headdress[1]
- hero[1]
- human figure[1]
- hunter[1]
- inscription[1]
- insect[1]
- king[5]
- leg[1]
- lion[4]
- lion?[1]
- man[1]
- necklace[1]
- pole[1]
- robe[2]
- seated figure[1]
- seated god[1]
- skirt[1]
- snake[1]
- standard[1]
- standing figure[1]
- star[1]
- star?[1]
- stick[1]
- vase[1]
- votary[1]
- agate[2]
- bitumen[1]
- bone[1]
- bronze[1]
- carnelian[13]
- ceramic[1]
- copper[1]
- copper alloy[1]
- diorite[1]
- egyptian blue[2]
- faience[4]
- flint[1]
- frit[4]
- glass[7]
- gold[3]
- hematite[3]
- jasper[1]
- lapis lazuli[8]
- marble (stone)[1]
- metal[2]
- paste[2]
- quartz[5]
- rock crystal[1]
- shell[15]
- silver[1]
- steatite[1]
- stone[336]
- terracotta[1]
- turquoise[1]
- carved[1]
- incised[4]
- inscribed[1]
- perforated[1]
- polished[2]
- actual citation[109]
1 - 30 of 336 Records






























1 - 30 of 336 Records


